Imagining a World Without Waste
Imagine a world without waste. A place where people prioritize repairing over replacing products. Everyday items are made from innovative materials designed for easy reuse and recycling. Picture a supply chain where advanced recycling technologies and smart return solutions create endless loops for goods. This is the future of circular supply chains.
Changing the Supply Chain Model
The traditional approach to production, sales, use, and disposal of products (linear economy) has become outdated. In the face of increasingly clear signs of climate change and environmental damage, the need to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions has become more urgent than ever. Using renewable energy sources and minimizing carbon are essential steps. However, there is another crucial factor: transitioning to a circular supply chain model (the circular economy). This holistic approach transforms one-directional supply chains into circular loops by optimizing production, developing new product usage models, and finding efficient recycling solutions.
The potential benefits of the circular economy are immense: research shows it can reduce emissions by up to 40% and be more economically efficient than any other carbon reduction methods. At the same time, it fosters innovation and growth.
Circular Supply Chains Have Huge Potential to Help Reach Net-Zero
For example, the fashion and consumer electronics industries should be prioritized for developing circular supply chains as they account for an estimated 6% of annual global greenhouse gas emissions—twice as much as aviation and nearly equal to the entire emissions of the European Union.
Therefore, extending the lifespan of clothing and electronics, reusing, and recycling their remaining value into production cycles is essential to mitigate the environmental impact of these industries.
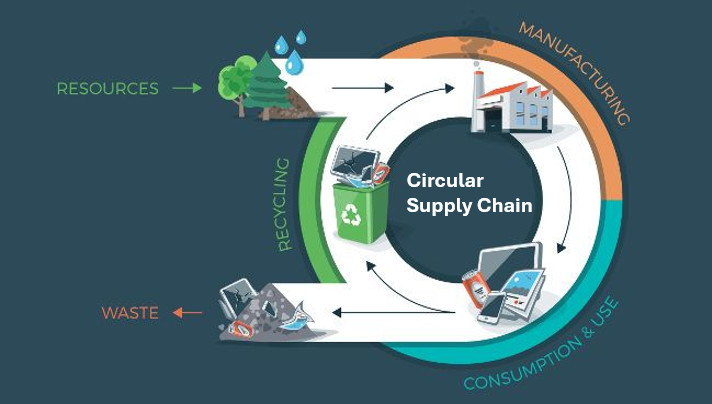
From "Reduce, Reuse, Recycle" to 5 Rs
In moving away from the old mantra "reduce, reuse, recycle," the circular economy demands a new model called the 5 Rs: reduce (produce fewer new products and use fewer new materials), repair (fix defects or damages), resell (sell products that are still functional but no longer used or needed), refurbish (return used products to manufacturers or service providers for inspection, cleaning, and restoration to their original state), and recycle. So, how can we promote and accelerate the transition to circular supply chains?
Building Efficient Circular Supply Chains
To further develop solutions for building circular supply chains, we can break down each element as follows:
1. Promoting Circular Consumption Behavior:
Organize educational and informational campaigns to help consumers understand the benefits of circular products and make smart choices. Additionally, develop e-commerce platforms or retail points with dedicated sections for recycled and reused products, along with discount policies or old product buyback programs for consumers.
2. Optimizing Reverse Logistics:
In a perfect circular ecosystem, goods are transported and returned in reusable packaging, optimizing the delivery and return process. Logistics providers have a significant opportunity to save costs and increase efficiency by combining different return flows. Companies can also support reverse logistics systems to enhance product value and lifespan through repairs or resales, thereby reducing waste and maximizing sustainability.
3. Investing in Research and Single-Material Production:
In many fields, manufacturers frequently use multiple materials and complex designs, making recycling difficult. Currently, some brands have adopted single-material design—using only one type of material to create products. This enhances recyclability. In the future, companies can use innovative, energy-efficient, and easily recyclable materials for production.
4. Lean Manufacturing:
In the future, the manufacturing process faces issues like material waste and wastewater. To promote the circular model, manufacturers need to develop solutions to minimize waste and maximize resource reuse, such as using wastewater for irrigation. Overproduction, for example, in the fashion industry, is a significant challenge when about 20% of products go unused. An effective solution is demand-driven production, combining inventory-free methods with eco-friendly technologies to customize products based on consumer needs.
By implementing these solutions comprehensively and effectively, businesses can build and manage circular supply chains to minimize environmental impact and enhance sustainability in their operations.
Circular Supply Chains: Collective Action Needed!
Promoting circular principles not only brings significant environmental benefits but also creates sustainable development opportunities for all stakeholders. To turn this vision into reality, close collaboration between brands, manufacturers, governments, consumers, and logistics providers is crucial. We need to create an environment that encourages consumers to choose circular products and simultaneously develop modern logistics infrastructure to efficiently manage these complex supply chains. Only through this collaboration can we achieve significant progress in reducing the environmental impact of industrial production and building a more sustainable future for future generations.
Source: Forbes, DHL Group