In inventory management and product information tracking, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and Barcode are two of the most widely used data collection methods today. Each technology has unique characteristics in terms of cost, implementation, and operational efficiency. So, what are the differences between RFID and Barcode? Which one is the most suitable choice for your business?
.jpg)
1. Introduction to RFID and Barcode
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, a technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify and track objects. RFID consists of two main components: RFID tags attached to the product and RFID readers to collect information from the tags.
Barcode technology uses barcodes printed on the product surface and barcode scanners to identify products. Barcodes usually contain basic product information, such as item codes, prices, and origins.
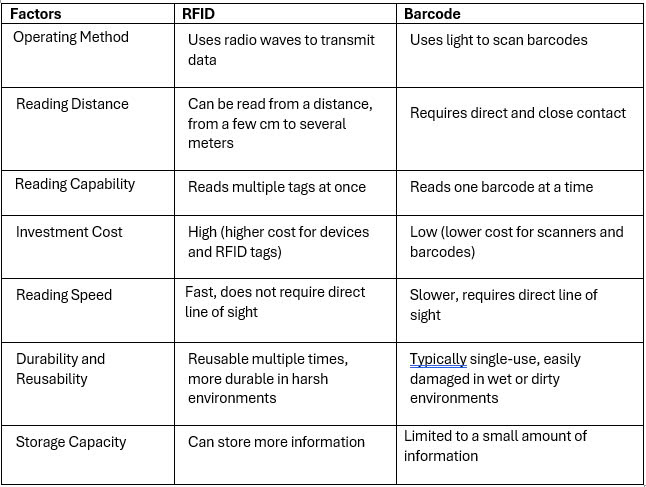
2. Differences between RFID and Barcode
3. Benefits and Limitations of Each Technology
RFID:
- Benefits:
- Remote Reading: Can read information from a distance without direct contact.
- High Speed and Efficiency: Can read multiple tags simultaneously, saving time.
- High Durability: Suitable for harsh environments where barcodes can get damaged.
- Limitations:
- High Investment Cost: Costs for devices, RFID tags, and system implementation are usually higher than barcodes.
- Radio Interference: Can face challenges in environments with a lot of radio wave interference.
Barcode:
- Benefits:
- Low Cost: Inexpensive devices and barcodes, easy to print and use.
- Simple and Easy to Implement: Does not require extensive technical infrastructure.
- Limitations:
- Manual and Slow Reading: Requires reading one barcode at a time, needing human intervention.
- Easily Damaged: Barcodes are easily damaged or smudged in harsh environments.
4. Impact on Your Business
- RFID is suitable for: Businesses that need high speed and efficiency in inventory management, asset management, or operate in harsh environments. This technology is particularly useful in retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics sectors.
- Barcode is suitable for: Smaller businesses with simple inventory needs and looking to save on investment costs. Barcodes are also ideal for supermarkets, small retail stores, where automation and speed are not critical.
5. Conclusion: Which is the Better Choice?
Choosing between RFID and Barcode depends on the specific needs and financial capabilities of your business. If you need a fast, accurate inventory management solution with a high investment capacity, RFID may be a better choice. However, for businesses looking to save costs and ensure effectiveness in a simple management environment, Barcode remains a reasonable solution.
At CJ Gemadept (CJ GMD), we currently apply barcode scanning technology to manage inventory. This method offers cost benefits, ease of implementation, and aligns well with our current warehouse management system. We are always ready to upgrade and explore new technological solutions to optimize processes, ensuring service quality and customer satisfaction.